Why Do Dogs Love Sleeping in Bed?
Why dogs like sleeping in bed? Many dog owners have experienced the joy of sharing their bed with their furry friends. But have you ever wondered why …
Read Article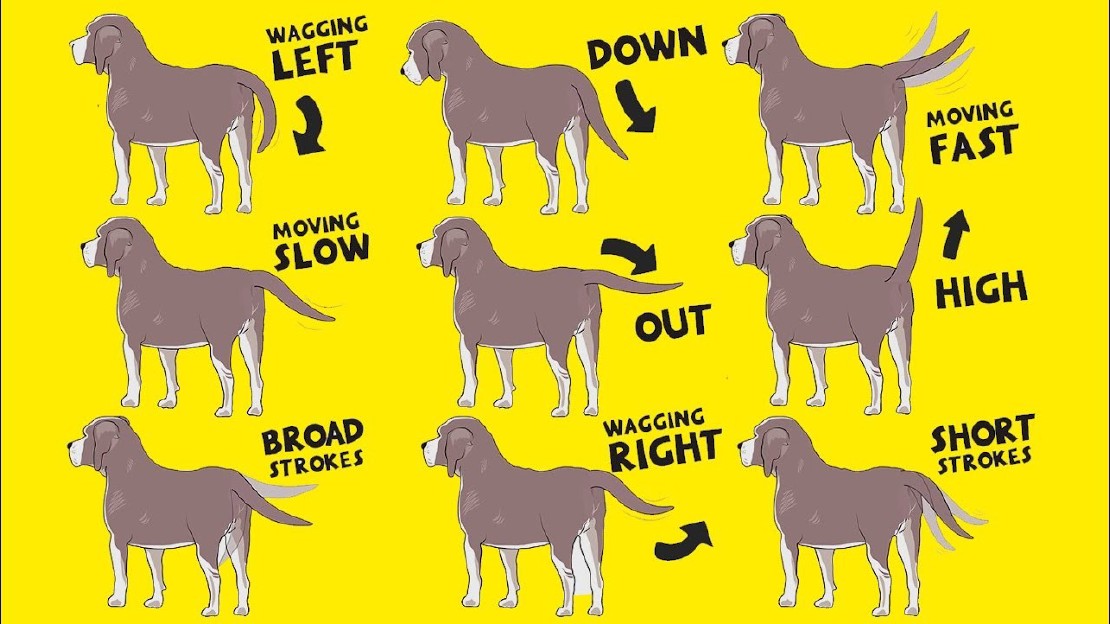
As humans, we often rely on verbal communication to express our thoughts and emotions. However, our furry companions, dogs, use a different language to communicate with us and each other. This language consists of various body signals, including growling and tail wagging. While these signals may seem contradictory, they hold significant meaning in a dog’s communication repertoire.
One of the most common misconceptions is that a wagging tail always indicates a happy and friendly dog. While this might be true in some cases, tail wagging can also be a sign of other emotions, such as fear, anxiety, or aggression. The position, speed, and intensity of the tail movements can provide important insights into a dog’s emotional state.
Growling, on the other hand, is often associated with aggression and hostility. However, growling can also be a dog’s way of expressing fear, discomfort, or pain. It is essential to look beyond the growling itself and consider the context and other body language cues to understand the true meaning behind this vocalization.
By learning to interpret a dog’s mixed signals, such as growling and tail wagging, we can gain a better understanding of their needs and emotions. It allows us to communicate effectively with our canine companions and ensure their well-being. In this article, we will explore the various factors that influence a dog’s communication signals and provide insights into deciphering their mixed signals.
When it comes to understanding our canine companions, it’s important to pay attention to the subtle cues they provide. Dogs communicate through a combination of body language, vocalizations, and facial expressions, but sometimes their signals can be confusing and conflicting.
One common example of mixed signals in dogs is when they growl while wagging their tail. On one hand, a wagging tail is often associated with happiness and friendliness, but growling is a clear indication of aggression or discomfort. So what does it mean when a dog displays both behaviors at the same time?
In most cases, when a dog growls while wagging their tail, it is a sign of fear or anxiety. The wagging tail may actually be a sign of appeasement, as the dog is trying to communicate that they are not a threat. However, the growling is a warning signal, indicating that the dog is feeling threatened or uncomfortable in some way.
It’s important to not interpret a wagging tail as an invitation to approach or interact with the dog when they are growling. This mixed signal means that the dog is giving conflicting messages and may not be receptive to attention or interaction at that moment.
If you encounter a dog displaying mixed signals like growling and wagging tail, it’s best to give them space and avoid any actions that may escalate their fear or anxiety. Instead, try to identify the source of their discomfort or threat and remove it if possible.
Remember, when it comes to understanding a dog’s mixed signals, it’s crucial to look at the whole picture and consider all their behaviors and body language cues. Consult with a professional trainer or behaviorist if you are unsure how to interpret your dog’s signals or if you need help addressing any behavioral issues.
Growling is a form of communication that dogs use to express their discomfort or displeasure. It can indicate that a dog is feeling threatened, fearful, or is in pain. It is important to pay attention to a dog’s body language along with the growling to get a better understanding of their intent.
Growling can be a warning sign that a dog is feeling disturbed or wants to establish boundaries. It is essential to respect a dog’s growl and give them space and time to calm down. It is not advisable to punish or scold a dog for growling as it may suppress their warning signs and lead to more aggressive behavior in the future.
In some cases, growling can also be a sign of fear or anxiety. It is crucial to identify the underlying cause of such behavior and address the issue with positive reinforcement training or professional help if needed. Ignoring or dismissing a dog’s growling can worsen their anxiety and fear, leading to more behavioral problems.
It is important to remember that not all growling is aggressive. Some dogs may growl during play, which is considered normal and should not be a cause for concern. However, it is essential to pay attention to the overall body language of the dog and ensure that the play remains appropriate and safe for everyone involved.
To understand the meaning of growling, it is crucial to consider the context, the dog’s body language, and their overall behavior. Seeking guidance from a professional dog trainer or behaviorist can be helpful in interpreting a dog’s mixed signals and ensuring their well-being.
A wagging tail is often seen as a sign of happiness and friendliness in dogs. However, it is important to understand that the wagging of a dog’s tail can have different meanings and interpretations depending on the context and other accompanying body language.
Speed of wagging: The speed at which a dog wags its tail can provide important clues about their emotional state. A fast wagging tail usually indicates excitement or joy, while a slow wagging tail can signify hesitation or uncertainty. It’s essential to pay attention to the speed of the wagging tail to gauge the dog’s overall mood.
Direction of wagging: The direction in which a dog wags its tail can also convey specific messages. If a dog’s tail is wagging in a relaxed, wide arc, it is likely feeling content and at ease. On the other hand, if the tail is stiff and only wagging slightly from side to side, it could be a sign of tension or potential aggression.
Position of the tail: The position of a dog’s tail can provide additional information about its emotional state. A high-held tail is often associated with confidence and alertness, while a tail held low can indicate submission or fear. It is important to consider the overall body language of the dog to accurately interpret the meaning behind the position of its tail.
Context and other body language: While the wagging tail is an important cue, it should always be considered in conjunction with the overall body language of the dog and the context in which it is occurring. For example, if a dog’s tail is wagging, but its body is tense and its ears are pinned back, it could be a sign of aggression or fear rather than happiness.
In conclusion, interpreting a wagging tail requires taking into account various factors such as the speed, direction, and position of the tail, as well as the overall body language and context. It is crucial to understand that a wagging tail does not always indicate friendliness or happiness and that other signs should be considered to accurately understand a dog’s emotional state. Being attentive and observant of a dog’s behavior can help ensure a positive and safe interaction with our furry friends.
Understanding a dog’s mixed signals, such as growling and wagging tail, can be a challenging task for dog owners. The contradiction between these two behaviors can be confusing, leading to misunderstandings and potentially dangerous situations.
When a dog growls, it is often interpreted as a sign of aggression or discomfort. Growling is a vocalization that dogs use to communicate their displeasure or warning. It can be a defensive response to perceived threats or a way for the dog to establish boundaries.
On the other hand, a wagging tail is commonly associated with happiness and friendliness in dogs. It is usually seen as an invitation for interaction and a sign of a positive emotional state. However, it is important to note that not all tail wagging is indicative of a friendly demeanor.
The contradiction arises when a dog is growling while also wagging its tail. This behavior can be perplexing and may lead some to believe that the dog is friendly despite the growling. It is crucial to recognize that in these cases, the dog’s aggression or discomfort is still present, even if the tail is wagging.
One possible explanation for this contradiction is that the dog may be displaying conflicting emotions. It could be feeling both threatened and excited or conflicted about its response to a particular situation. In these instances, it is essential to proceed with caution and avoid approaching the dog or engaging in any sudden movements.
It is always advisable to seek the assistance of a professional dog behaviorist or trainer in such situations. They can help assess the dog’s behavior and provide guidance on the appropriate steps to take. Remember, it is better to err on the side of caution when it comes to interpreting a dog’s mixed signals to ensure the safety of both the dog and the humans around them.
When a dog growls, it can be due to either aggression or fear. Aggressive growls are usually low, deep, and accompanied by a tense body posture. The dog may also show other signs of aggression, such as bared teeth or raised hackles. On the other hand, fearful growls are often higher-pitched and accompanied by submissive body language, such as cowering or tucking the tail between the legs. It’s important to consider the context and other body signals to determine whether a dog is growling out of aggression or fear.
No, a wagging tail is not always a sign of a happy dog. While it is commonly associated with happiness, the meaning behind a wagging tail can vary depending on the context and other body signals. For example, a slow and stiff wag may indicate that the dog is feeling cautious or on guard. Conversely, a fast and loose wag usually reflects excitement or friendliness. The position of the tail can also provide important information. A high and rigid tail may indicate dominance or aggression, while a low and relaxed tail is often a sign of relaxation or submission.
If you encounter a growling dog, it’s important to prioritize your safety. Do not make sudden movements or run away, as this can escalate the situation. Instead, stand still and avoid direct eye contact with the dog. If possible, slowly and calmly back away while keeping the dog in your peripheral vision. It’s best to let the dog approach or sniff you on its own terms, without making any sudden gestures. If the dog shows signs of aggression, such as lunging or snapping, it’s important to seek professional help from a qualified dog behaviorist or trainer.
Yes, a wagging tail can be a sign of nervousness or anxiety in some dogs. While tail wagging is often associated with positive emotions, it can also occur in stressful situations. Nervous or anxious dogs may exhibit a rapid or low-set wag, along with other signs of stress such as panting, pacing, or hiding. These dogs may wag their tails as a self-soothing behavior or a way of communicating their discomfort. It’s important to observe the overall body language and context to determine whether a wagging tail is a sign of happiness or anxiety.
Why dogs like sleeping in bed? Many dog owners have experienced the joy of sharing their bed with their furry friends. But have you ever wondered why …
Read ArticleWhy dogs kick dirt after pooping? Dogs have many unique and interesting behaviors, and one of these fascinating actions is when they kick dirt after …
Read ArticleWhy dogs eat their puppies? One of the most shocking and puzzling behaviors observed in domestic dogs is when a mother dog eats her own puppies. This …
Read ArticleWhy dog puts paw on you? Have you ever noticed that your dog often puts its paw on you? This behavior might seem cute or endearing, but have you ever …
Read ArticleWhy is my dog panting with his mouth open? Table Of Contents Common Reasons for Dogs Panting with Their Mouth Open Heat and Overexertion Anxiety and …
Read ArticleWhy is my puppys tummy gurgling? As a puppy owner, you may have noticed your furry friend’s tummy making strange gurgling sounds from time to …
Read Article