Why do dogs lick your face?
Why dogs lick your face? Dogs are known for their affectionate nature and one common way they show their love is by licking their owners’ faces. …
Read Article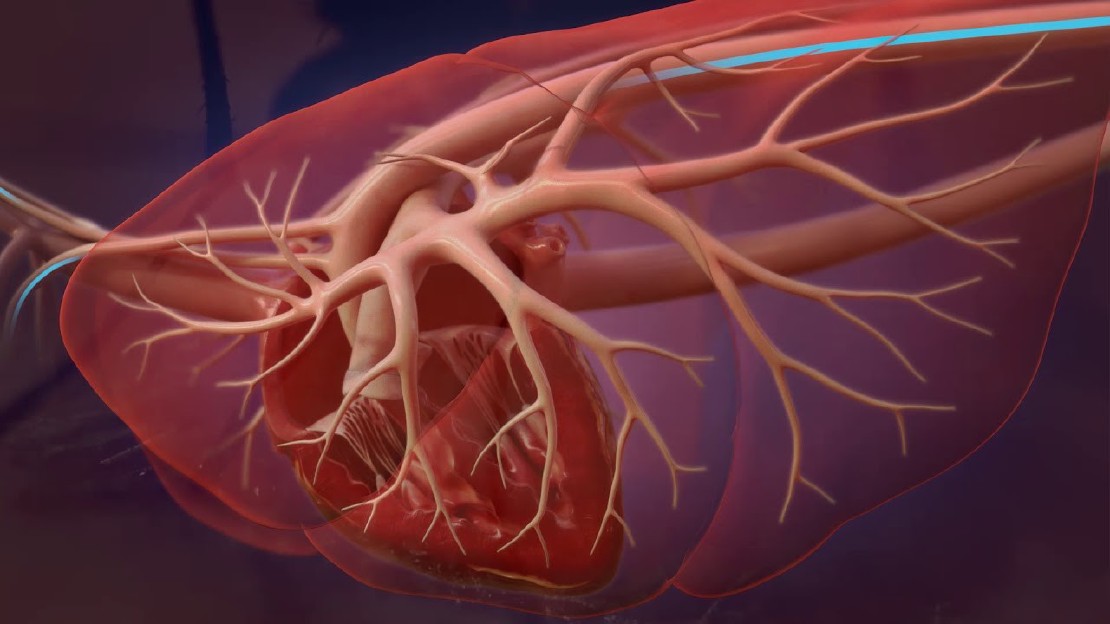
Heartworm disease is a serious and potentially fatal condition that affects dogs of all ages, breeds, and sizes. It is caused by the parasitic worm, Dirofilaria immitis, which is transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes. Once infected, the worms live in the heart, lungs, and blood vessels of the dog, causing significant damage to these vital organs.
Heartworm disease can have a devastating impact on dogs’ health and wellbeing, leading to symptoms such as coughing, difficulty breathing, fatigue, and weight loss. If left untreated, it can progress to severe complications, including heart failure and organ damage. Unfortunately, heartworm disease is widespread in many parts of the world, making it a common concern for dog owners and veterinarians.
Prevention is key when it comes to heartworm disease. Regular testing, proper vaccination, and consistent use of preventive medications are essential to keeping dogs safe. Additionally, understanding the risk factors associated with heartworm disease, such as living in a mosquito-prone area or having a dog that spends time outdoors, can help dog owners take proactive measures to protect their pets.
It is important for dog owners to be knowledgeable about heartworm disease and its impact on dogs. By educating ourselves and taking preventive measures, we can ensure the health and longevity of our furry friends.
Heartworm disease is a serious and potentially fatal condition that affects dogs. It is caused by a parasitic worm known as Dirofilaria immitis, which is transmitted through mosquito bites.
Once infected, the heartworm larvae migrate to the heart and lungs, where they mature into adult worms. These worms can grow up to 12 inches in length and can live for several years in the dog’s body.
Heartworm disease can have a detrimental impact on a dog’s health. The worms can cause blockages in the arteries and restrict blood flow, leading to heart and lung damage. The disease can also cause inflammation and scarring of the heart, leading to heart failure.
Common symptoms of heartworm disease include coughing, difficulty breathing, fatigue, and weight loss. In severe cases, dogs may experience fainting or collapse. However, early stages of the disease may present no visible symptoms, making regular testing and prevention crucial.
Prevention and treatment of heartworm disease are available and should be discussed with a veterinarian. Preventive measures include administering monthly medication that kills heartworm larvae and regular testing to catch the disease in its early stages. Treatment for infected dogs may involve medication to kill the adult worms, as well as other supportive care measures.
Heartworm disease is a serious threat to the health and well-being of dogs. By understanding the disease and taking preventive measures, pet owners can help ensure the longevity and quality of life for their furry friends.
Heartworm disease is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects dogs of all ages and breeds. The disease is caused by a parasitic worm called Dirofilaria immitis, which is transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes. While heartworms primarily affect the heart and lungs, they can also invade other organs, leading to a range of symptoms.
One early sign of heartworm disease is a persistent cough. Dogs with heartworms may cough repeatedly, particularly after physical activity or excitement. This cough is caused by inflammation and irritation in the airways due to the presence of the parasites. Additionally, dogs may exhibit shortness of breath and weakness, as the heart and lungs become compromised by the presence of the worms.
As the disease progresses, dogs may experience weight loss despite having a good appetite. This is because the heartworms disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system, leading to malnutrition. Dogs may also have a decreased interest in exercise and may tire easily. In severe cases, dogs may develop a swollen abdomen due to fluid accumulation, as the heart struggles to pump blood effectively.
In some cases, heartworm disease can lead to more severe complications, including heart failure and collapse. Dogs may develop a bluish tint to their gums and tongue, indicating poor oxygen circulation. If left untreated, heartworm disease can be fatal.
If you notice any of these signs or symptoms in your dog, it is important to seek veterinary care as soon as possible. A veterinarian can perform a blood test to diagnose heartworm disease, and treatment options may include medication to kill the worms and manage the symptoms. Preventative measures, such as regular heartworm prevention medication and avoiding exposure to mosquitoes, can help protect your dog from this dangerous disease.
Preventing heartworm disease is crucial for the overall health and well-being of dogs. The best way to prevent heartworm disease is through monthly administration of a heartworm preventive medication prescribed by a veterinarian.
Heartworm preventive medications work by killing the immature larvae, known as microfilariae, that are transmitted to dogs through mosquito bites. These medications are available in different forms, including chewable tablets, topical spot-on treatments, and injectables.
It is important to administer heartworm preventive medications consistently and on time to ensure maximum effectiveness. Regular heartworm testing is also recommended, as it can detect infections in the early stages when treatment is more successful.
If a dog is diagnosed with heartworm disease, treatment can be complex and costly. The treatment typically involves a series of injections that kill the adult heartworms in the dog’s bloodstream. Additionally, medications to reduce inflammation and prevent further infection may be prescribed.
During the treatment process, it is essential to restrict a dog’s physical activity to minimize the risk of complications. A veterinarian will provide specific instructions on the post-treatment care, which may include follow-up testing to ensure the infection has been successfully treated.
Preventing heartworm disease through regular use of preventive medications is the best approach. By protecting dogs from heartworm infection, pet owners can help ensure their furry companions live long and healthy lives.
Heartworm disease is a serious and potentially fatal condition that affects dogs. It is caused by parasitic worms that live in the heart and lungs of infected animals.
Dogs get infected with heartworms through the bite of an infected mosquito. The mosquito serves as a carrier for the parasites, which then enter the dog’s bloodstream and eventually reach the heart and lungs.
The symptoms of heartworm disease in dogs can vary, but often include coughing, difficulty breathing, fatigue, weight loss, and a decreased appetite. In severe cases, dogs may experience heart failure and collapse.
Yes, heartworm disease can be prevented through the use of monthly heartworm preventives. These medications are prescribed by veterinarians and are highly effective in protecting dogs from heartworm infection.
Why dogs lick your face? Dogs are known for their affectionate nature and one common way they show their love is by licking their owners’ faces. …
Read ArticleWhy dogs are more loyal than cats? Dogs have long been known as man’s best friend, and their loyalty is one of the key reasons for this title. …
Read ArticleWhy is my dog poop green and slimy? Seeing green and slimy poop in your dog’s stool can be alarming, but it is important to understand that …
Read ArticleWhy is the side of my dogs mouth swollen? Swelling on the side of a dog’s mouth can be a cause for concern for pet owners. There are several …
Read ArticleWhy is my dog panting when it isnt hot? Panting is a natural behavior for dogs, as it helps them regulate their body temperature. However, if your dog …
Read ArticleWhy is my senior dog barking all the time? As your dog ages, you may start to notice changes in their behavior, one of which may be excessive barking. …
Read Article