Why Do Dogs Love Sleeping in Bed?
Why dogs like sleeping in bed? Many dog owners have experienced the joy of sharing their bed with their furry friends. But have you ever wondered why …
Read Article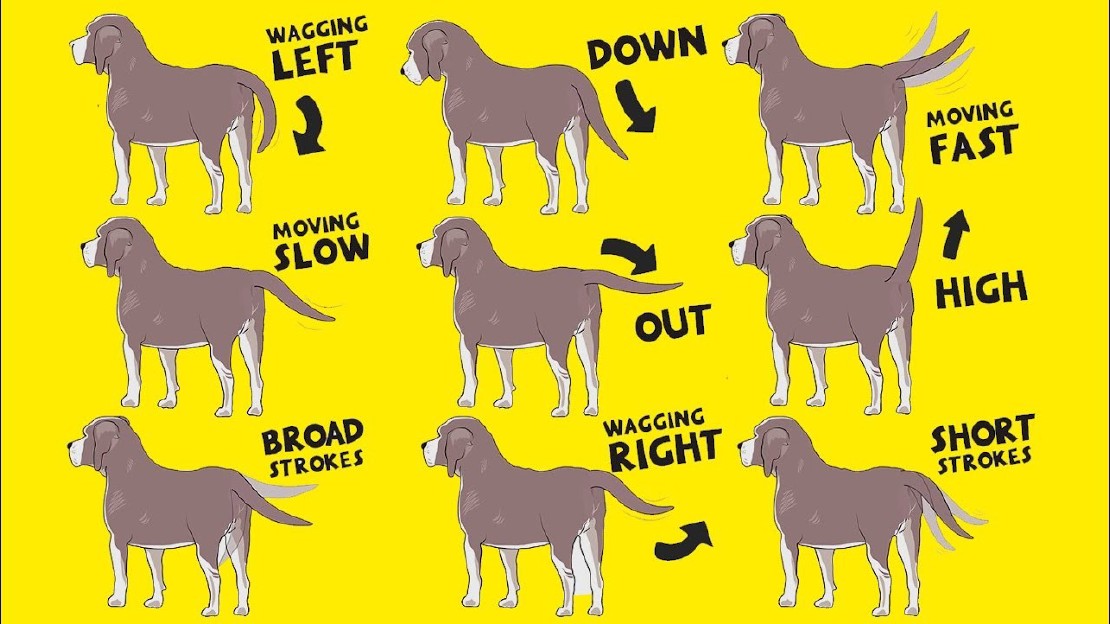
Dogs use their tails to communicate a wide range of emotions and intents. From happiness and excitement to fear and aggression, the position and movement of a dog’s tail can provide valuable insights into their state of mind. However, understanding the nuances of dog tail language can be a bit tricky, as different tail wags can convey different meanings.
When a dog’s tail is wagging in a loose and relaxed manner, it usually indicates a friendly and happy demeanor. This type of wag is often accompanied by a relaxed body posture and a wagging rear end. On the other hand, a stiff and rigid tail wag may be a sign of caution or even aggression. It’s important to pay attention to the overall body language of the dog to correctly interpret the meaning behind the tail wag.
The position of a dog’s tail also plays a significant role in determining its meaning. A high, raised tail can denote confidence and dominance, while a low or tucked tail indicates fear or submission. A furiously wagging tail held high suggests excitement, while a tail tucked tightly between the legs could indicate anxiety or distress.
It’s worth noting that tail language can vary among different dog breeds, and individual dogs may have their own unique tail behaviors. Being aware of these individual variations and familiarizing oneself with the general principles of dog tail language can help build better understanding and communication with our furry companions.
Dogs use their tails as a way to communicate with humans and other animals. By observing their tail movements, we can get a better understanding of a dog’s emotions and intentions. Each wag or position of the tail can convey a different message, allowing us to decode their tail language.
1. Wags and Speed: The speed of a dog’s tail wag can indicate their level of excitement or arousal. A fast wagging tail usually means the dog is happy and friendly. On the other hand, a slow wag or a stiff, rigid tail may indicate caution or aggression.
2. Tail Height and Position: The height and position of a dog’s tail can also provide valuable information about their mood. A high, raised tail typically signifies confidence and alertness, while a lowered or tucked tail may indicate fear or submission. A tail held straight out from the body could indicate tension or uncertainty.
3. Direction of the Wag: The direction in which a dog wags their tail can also have meaning. A tail wagging to the right often indicates a positive and friendly disposition, while a tail wagging to the left can indicate anxiety or potential aggression. However, it’s important to consider the overall context and body language to accurately interpret a dog’s wagging tail.
4. Stillness and Stiffness: A still tail held high and rigid can be a sign of alertness or potential aggression. On the other hand, a relaxed and loose tail usually suggests that the dog is calm and comfortable. Pay attention to any stiffness or tension in the tail, as it could indicate unease or stress.
Learning to understand dog tail language can help us better interact with and read our canine companions. However, it’s important to remember that tail movements should always be interpreted in conjunction with other body language cues to accurately assess a dog’s emotional state.
Tail language refers to the various movements and positions of a dog’s tail, which serve as important communication signals. Dogs use their tails to express a range of emotions and intentions, and understanding tail language can help humans better interpret their dogs’ behavior.
When a dog wags its tail, it is often seen as a sign of happiness and excitement. However, tail wagging can also indicate other emotions depending on the speed, height, and direction of the wag. Dogs may wag their tails rapidly when they are excited or happy, while a slow wag or a tail held low may indicate fear or uncertainty.
The position of a dog’s tail can also provide information about their mood. A high, raised tail typically indicates confidence and alertness, while a tucked tail between the hind legs can indicate fear or submission. Some dogs have naturally high-set tails, so it’s important to consider their overall body language and context to understand their emotions accurately.
In addition to wagging and positioning, the stiffness or looseness of a dog’s tail can also convey meaning. A stiff tail held upright often signals alertness or aggression, while a relaxed and loose tail suggests a calm and friendly demeanor. It’s important to note that tail language should always be interpreted in conjunction with other body language signals to get a complete understanding of a dog’s emotions.
Overall, being able to read a dog’s tail language can enhance the communication between dogs and their human companions. It allows humans to better understand a dog’s needs, emotions, and intentions, leading to stronger bonds and healthier relationships. Observing and interpreting tail language can contribute to a more fulfilling and harmonious life with our canine friends.
When it comes to decoding a dog’s body language, the position and movement of their tail can reveal a lot about their feelings and intentions. While tail wagging is often associated with happiness and friendliness, it’s important to note that different tail wags can convey different messages.
1. Vertical Tail Wag: A dog with their tail held high and wagging in a vertical position is usually feeling confident and assertive. This tail position can often be seen when a dog is meeting new people or animals and is trying to show dominance. They may be alert and ready to take charge if necessary.
2. Horizontal Tail Wag: When a dog’s tail is held parallel to the ground and wagging back and forth, it typically indicates a friendly and sociable attitude. This is often the tail wag that owners love to see as it signifies a happy and content dog. It’s a good sign that the dog is open to interaction and is comfortable in their environment.
3. Low Tail Wag: A dog wagging their tail low or between their legs may be expressing fear, anxiety, or submission. This tail position suggests a lack of confidence and a desire to avoid confrontation. It’s important to approach a dog with a low tail wag cautiously and provide them with space and reassurance.
4. Fast Tail Wag: A rapid and vigorous tail wag usually indicates excitement. This can be seen when a dog is happy to see their owner, anticipating playtime, or about to engage in an activity they enjoy. It’s a sign of positive energy and enthusiasm.
5. Slow Tail Wag: On the other hand, a slow and deliberate tail wag can indicate caution and uncertainty. It may be a signal that the dog is unsure about a situation or feeling a bit wary. Owners should be mindful of this tail wag and try to create a calm and safe environment for their dog.
6. Stiff Tail Wag: When a dog’s tail is wagging stiffly and with little movement, it can be a sign of tension or aggression. This tail position suggests that the dog is on guard and may be ready to react defensively. It’s important to read the other body language cues in conjunction with the tail wag to accurately interpret the dog’s intentions.
In conclusion, understanding and interpreting a dog’s tail wags can provide valuable insights into their emotions and behavior. By paying attention to the position, speed, and overall body language, we can better communicate with and respond to our furry friends.
In addition to tail wagging, dogs use various other cues to communicate their emotions and intentions. One important clue is ear position. When a dog’s ears are relaxed and facing forward, it generally indicates that the dog is curious or interested. On the other hand, if the ears are pinned back against the head, it can be a sign of fear or aggression. Dog owners should pay attention to the position of their dog’s ears to better understand their mood.
Another important aspect of dog body language is posture. A dog standing tall and erect, with its weight balanced evenly on all four legs, is typically confident and alert. On the contrary, a dog with a lowered body posture, crouching or tucking its tail between its legs, is often displaying fear or submission. Understanding these postural cues can help dog owners determine how their pet is feeling in different situations.
Facial expressions also play a significant role in dog body language. Just like humans, dogs can convey various emotions through their facial expressions. For example, a relaxed and open mouth with a slightly lolling tongue often means the dog is content and relaxed. On the other hand, a snarling or baring of teeth is a clear sign of aggression. By paying attention to these facial cues, dog owners can better interpret their dog’s emotions and respond accordingly.
Finally, body movement and overall energy can also provide important clues about a dog’s mood. A dog that is constantly jumping, spinning, or wagging its tail vigorously is likely to be excited or happy. Conversely, a slow and deliberate movement, along with a stiff body posture, may indicate that the dog is cautious or on guard. By observing these subtle cues in a dog’s body language, owners can enhance their ability to communicate effectively with their furry friends.
Common tail movements in dogs include wagging, tucking, stiffening, and raising. Wagging usually means the dog is happy and friendly, tucking indicates fear or submission, stiffening signals aggression or alertness, and raising can indicate excitement or dominance.
If your dog’s tail is tucked between their legs, it typically means they are scared or anxious. Additionally, if their tail is stiff and held low or between their legs, it can also indicate fear or anxiety. Other signs to look for include a low body posture, ears pinned back, and avoidance behavior.
If a dog’s tail is wagging but their body is tense, it can indicate mixed emotions. They may be excited but also on guard or unsure. It’s important to assess the situation and the dog’s overall body language to determine their true emotional state.
Yes, in some cases, a dog’s tail wagging can actually be a sign of aggression. If the tail is stiff or held high, accompanied by other aggressive body postures such as raised hackles or bared teeth, it may indicate a potentially aggressive or dominant behavior. It’s crucial to consider the complete context and the dog’s overall body language to accurately interpret their intentions.
Why dogs like sleeping in bed? Many dog owners have experienced the joy of sharing their bed with their furry friends. But have you ever wondered why …
Read ArticleWhy dogs kick dirt after pooping? Dogs have many unique and interesting behaviors, and one of these fascinating actions is when they kick dirt after …
Read ArticleWhy dogs eat their puppies? One of the most shocking and puzzling behaviors observed in domestic dogs is when a mother dog eats her own puppies. This …
Read ArticleWhy dog puts paw on you? Have you ever noticed that your dog often puts its paw on you? This behavior might seem cute or endearing, but have you ever …
Read ArticleWhy is my dog panting with his mouth open? Table Of Contents Common Reasons for Dogs Panting with Their Mouth Open Heat and Overexertion Anxiety and …
Read ArticleWhy is my puppys tummy gurgling? As a puppy owner, you may have noticed your furry friend’s tummy making strange gurgling sounds from time to …
Read Article