Reasons why your dog has stopped drinking water
Why has my dog stopped drinking water? Water is an essential part of your dog’s health and well-being. However, if you notice that your dog has …
Read Article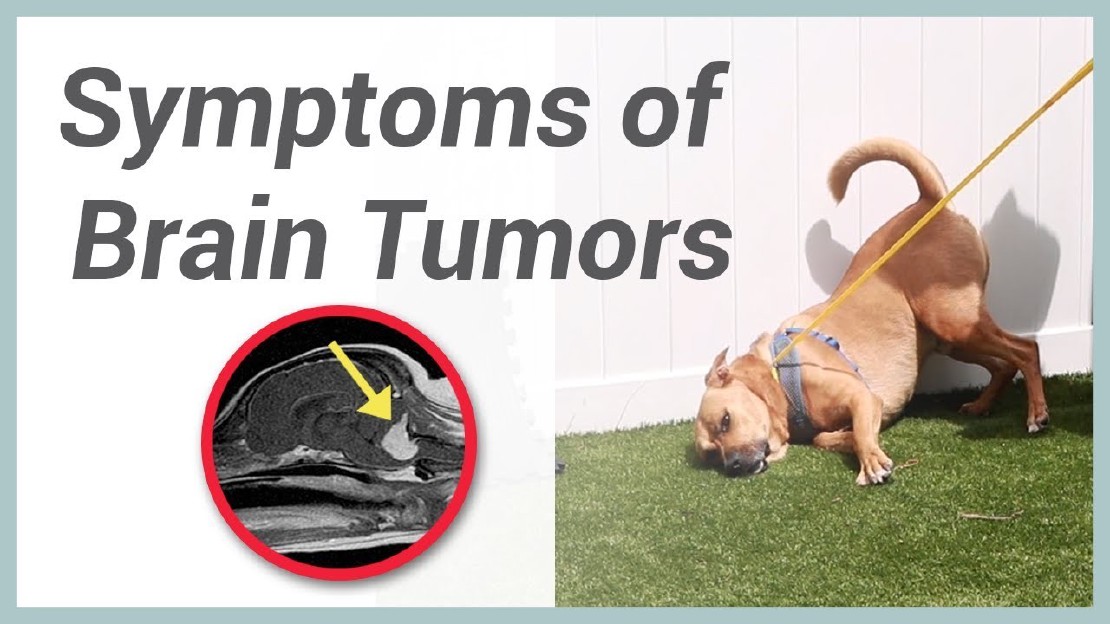
Neurological disorders in dogs can be a distressing occurrence for both the canine and their owners. These disorders can have a wide range of causes, which can make determining the exact reason behind a specific disorder challenging. However, understanding the potential causes of neurological disorders in dogs can help veterinarians and owners manage and prevent these conditions.
One of the leading causes of neurological disorders in dogs is genetics. Certain breeds are predisposed to specific neurological conditions, and often, these disorders are passed down through generations. For example, certain types of epilepsy are more prevalent in certain breeds, such as the Border Collie. Understanding the genetic factors contributing to neurological disorders can help breeders make informed decisions when it comes to breeding practices.
Environmental factors can also play a significant role in the development of neurological disorders in dogs. Exposure to toxins and chemicals, such as lead or pesticides, can damage the nervous system and lead to various neurological symptoms. Traumatic injuries, such as head trauma or spinal cord injuries, can also result in neurological disorders. Identifying and minimizing exposure to these environmental factors can help reduce the risk of neurological disorders in dogs.
Infectious diseases can also cause neurological disorders in dogs. Certain viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections can invade the nervous system and cause inflammation or damage. For example, canine distemper virus is notorious for its potential to cause neurological symptoms in infected dogs. Vaccinations and preventive measures can help protect dogs from these infectious causes of neurological disorders.
In conclusion, the causes of neurological disorders in dogs are multifaceted and can include genetic factors, environmental factors, and infectious diseases. Understanding these causes is essential for prevention, early detection, and management of these conditions. By working closely with veterinarians and implementing preventive measures, dog owners can help ensure their pets live healthy, happy lives free from neurological disorders.
Neurological disorders in dogs can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, infections, trauma, and metabolic disorders. These conditions can affect the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, as well as the peripheral nervous system, which includes the nerves that connect the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body.
Genetic factors can play a significant role in the development of neurological disorders in dogs. Certain breeds are more prone to genetic conditions that affect the nervous system, such as epilepsy, degenerative myelopathy, and cerebellar ataxia. In some cases, genetic mutations can cause abnormal growth or function of the nerves, leading to neurological symptoms.
Infections can also cause neurological disorders in dogs. Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can all affect the nervous system, causing inflammation and damage to the nerves. Some common infections that can lead to neurological symptoms in dogs include distemper, rabies, and meningitis.
Trauma, such as being hit by a car or experiencing a fall, can result in neurological disorders. In these cases, the impact can cause damage to the brain or spinal cord, leading to a range of symptoms depending on the location and severity of the injury. Traumatic brain injury can cause symptoms such as seizures, loss of coordination, and changes in behavior.
Metabolic disorders, such as liver or kidney disease, can also contribute to the development of neurological disorders in dogs. These conditions can affect the body’s ability to regulate important substances, such as electrolytes, which are necessary for proper nerve function. When there is an imbalance or buildup of these substances, it can lead to neurological symptoms.
In conclusion, there are various causes of neurological disorders in dogs, including genetic factors, infections, trauma, and metabolic disorders. It is important for dog owners to be aware of these potential causes and seek veterinary care if their dog shows any signs of neurological symptoms.
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of neurological disorders in dogs. In many cases, certain breeds are predisposed to certain conditions due to their unique genetic makeup. For example, certain breeds of dogs are more prone to develop epilepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures. This is believed to be due to a genetic mutation that affects the brain’s electrical activity.
In addition to breed-specific genetic factors, there are also certain genetic mutations that can occur in any breed of dog, leading to neurological disorders. These mutations can affect various aspects of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. One example is the mutation that causes degenerative myelopathy, a progressive disease that affects the spinal cord and leads to weakness and paralysis in the hind legs.
Genetic factors can also influence the severity and progression of neurological disorders. In some cases, a particular mutation may cause a milder form of a disorder, while in others, it may lead to a more severe form. The inheritance pattern of the mutation can also impact the likelihood of a dog developing the disorder. Some mutations are inherited in a dominant manner, meaning that a dog only needs to inherit one copy of the mutated gene to be affected. Others are inherited in a recessive manner, meaning that a dog needs to inherit two copies of the mutated gene to be affected.
Understanding the genetic factors involved in neurological disorders in dogs is important for several reasons. Firstly, it can help with the development of genetic tests that can identify dogs at risk for specific disorders. This can allow breeders to make informed decisions about which dogs to breed, reducing the prevalence of these disorders in future generations. Secondly, it can help researchers better understand the underlying mechanisms of these disorders, leading to the development of more effective treatments and therapies.
Environmental influences play a significant role in the development and progression of neurological disorders in dogs. Factors such as exposure to toxins, infectious agents, and traumatic events can all contribute to the onset of these conditions.
Toxins: Dogs can be exposed to a wide range of toxins in their environment, including pesticides, heavy metals, and certain household chemicals. These toxins can enter the body through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact, and can have a detrimental effect on the nervous system. For example, lead poisoning can lead to neurological symptoms such as seizures and ataxia.
Infectious Agents: Certain infectious agents, such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites, can also cause neurological disorders in dogs. For instance, the canine distemper virus can affect the central nervous system, leading to symptoms such as muscle twitches and seizures. Tick-borne diseases, such as Lyme disease, can also cause neurological symptoms in dogs.
Traumatic Events: Traumatic events, such as head injuries or spinal cord injuries, can result in neurological disorders in dogs. These injuries can cause damage to the brain or spinal cord, leading to a wide range of symptoms depending on the location and severity of the injury. For example, a dog who experiences a spinal cord injury may develop paralysis or loss of sensation in their limbs.
In conclusion, environmental influences can greatly impact the development and progression of neurological disorders in dogs. It is important for dog owners to be aware of these potential influences and take steps to minimize their dog’s exposure to toxins, prevent infections, and provide a safe environment to reduce the risk of traumatic events. Regular veterinary check-ups and prompt treatment of any potential neurological symptoms can also help to diagnose and manage these disorders at an early stage.
Inflammatory conditions in dogs can affect the central nervous system and result in various neurological disorders. These conditions can be caused by infections, autoimmune reactions, or other inflammatory responses in the body.
Infections such as canine distemper, fungal infections, or bacterial meningitis can lead to inflammation in the brain and spinal cord, causing symptoms like seizures, coordination problems, and changes in behavior. Treatment for these conditions often involves antibiotics or antifungal medications to target the underlying infection.
Autoimmune conditions like meningitis, encephalitis, or polyradiculoneuritis occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the cells of the nervous system. This can lead to inflammation, nerve damage, and neurological symptoms. Treatment for autoimmune conditions typically involves immune-suppressing medications to suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation.
Inflammation can also occur as a response to trauma or injury to the nervous system. This can result in conditions like spinal cord inflammation or brain swelling, which can cause varying degrees of neurological dysfunction. Treatment for these inflammatory conditions may involve corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Some common neurological disorders in dogs include epilepsy, intervertebral disc disease, brain tumors, and degenerative myelopathy.
The possible causes of neurological disorders in dogs can vary. They can be genetic, such as in the case of some hereditary neurological diseases. Infections, such as canine distemper virus or tick-borne diseases, can also cause neurological problems. Traumatic injuries, exposure to toxins, or certain medications can also result in neurological disorders.
While not all neurological disorders in dogs can be prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk. This includes regular veterinary care, vaccinations to prevent infections, and preventing trauma or exposure to toxins. In some cases, breed-specific genetic testing can help identify dogs at risk for certain neurological disorders.
The diagnosis of neurological disorders in dogs often involves a combination of physical examinations, neurological examinations, and diagnostic tests. These tests can include blood work, imaging studies like X-rays or MRI scans, cerebrospinal fluid analysis, and occasionally, biopsies of affected tissues.
Why has my dog stopped drinking water? Water is an essential part of your dog’s health and well-being. However, if you notice that your dog has …
Read ArticleWhy has my dog started snarling at other dogs? It can be quite alarming when your normally friendly and well-behaved dog suddenly starts snarling at …
Read ArticleWhy is my dog pooping clear gel? Seeing your dog poop clear gel can be a cause for concern, and you may be wondering what could be causing this …
Read ArticleWhy is the bush dog endangered? The bush dog, also known as the Savannah dog or the vineyard dog, is a small and elusive mammal native to the forests …
Read ArticleWill lettuce hurt my dog? Dogs are known for their love of food and their ability to eat almost anything. However, when it comes to certain types of …
Read ArticleWhen can puppies leave the whelping box? Deciding when to separate puppies from their mother and the whelping box is a crucial decision that every …
Read Article