Why do dogs lick your face?
Why dogs lick your face? Dogs are known for their affectionate nature and one common way they show their love is by licking their owners’ faces. …
Read Article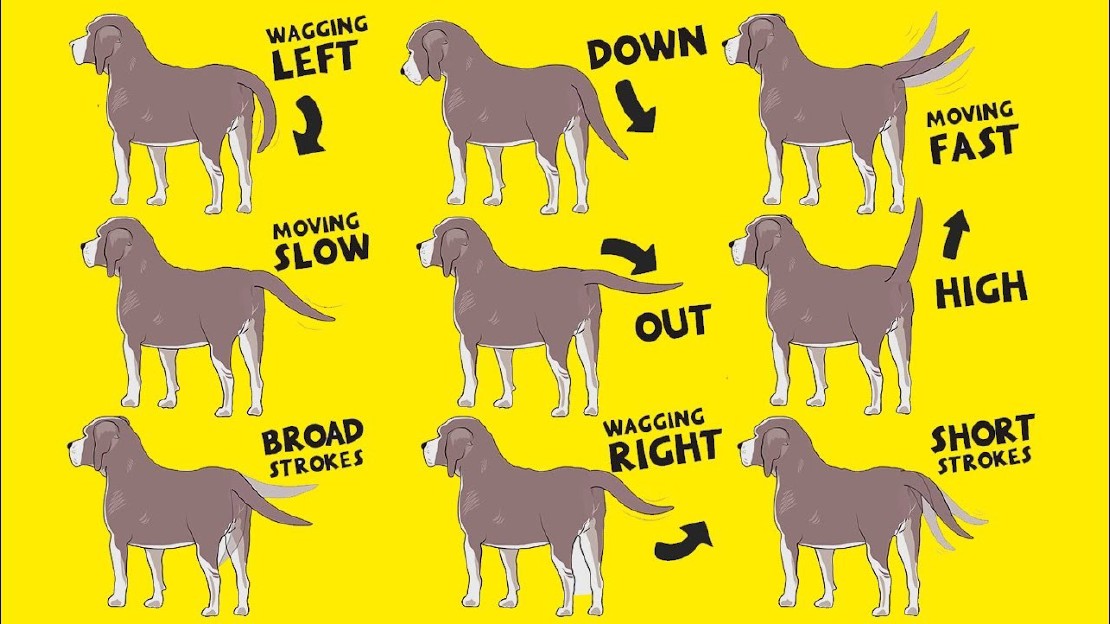
A dog’s tail is a remarkable appendage that plays a vital role in their communication and overall well-being. While it may seem like just another part of their anatomy, a dog’s tail is a complex structure that is highly sensitive and serves various purposes.
One significant aspect of a dog’s tail is its ability to express their emotions and intentions. Dogs have the remarkable ability to communicate through tail wagging, and each movement has a specific meaning. For example, a gentle wag from side to side is often associated with contentment or friendliness, while a stiff and rapid wag can signal excitement or arousal. Understanding the nuances of tail wagging can help us interpret a dog’s mood and respond accordingly.
In addition to communication, a dog’s tail also plays a crucial role in their balance and coordination. The tail acts as a counterweight, especially when a dog is performing agile movements or making sharp turns. It helps them maintain stability and navigate their surroundings effectively, whether they are running, jumping, or climbing. Tail sensitivity is essential in these situations, as it allows dogs to make quick adjustments and maintain their equilibrium.
Furthermore, a dog’s tail sensitivity can also indicate their general physical well-being. Dogs are known to be highly attuned to changes in their environment, and their tail can be a barometer for their overall health. Any sudden changes in tail movement or position, such as a drooping or stiffened tail, could indicate pain, discomfort, or even injury. By being aware of their tail sensitivity, we can quickly identify any health issues and seek appropriate veterinary care.
All in all, a dog’s tail is not just a cute feature; it is an essential tool for their communication, balance, and overall well-being. By understanding and respecting a dog’s tail sensitivity, we can deepen our bond with these incredible creatures and ensure their physical and emotional wellness.
A dog’s tail is not just a wagging appendage; it plays a vital role in their communication, emotions, and overall well-being. Dogs have a highly sensitive tail that serves as an important sensory organ, allowing them to convey various messages and understand their environment.
The sensitivity of a dog’s tail lies in the numerous nerve endings present in this appendage. These nerves enable dogs to detect changes in air flow, temperature, and even subtle vibrations. By wagging their tail up, down, or in a specific pattern, dogs can express a wide range of emotions, including happiness, excitement, fear, or anxiety.
It is essential for dog owners to be aware of their pet’s tail sensitivity and understand how to interpret its movements. For example, a relaxed and loose tail is often a sign of a content and calm dog, while a tucked tail indicates fear or submission. On the other hand, a stiff and erect tail can signify aggression or alertness.
Additionally, tail sensitivity can vary among different dog breeds. Some breeds, such as Greyhounds, have thin and delicate tails that may be more prone to injury. It is crucial to handle a dog’s tail with care to avoid causing them discomfort or pain. Gentle strokes and avoiding pulling or tugging on the tail can help maintain a positive and trusting relationship with your furry companion.
Understanding a dog’s tail sensitivity is essential for effective communication and building a strong bond with your pet. By paying attention to their tail movements and treating it with care, you can better understand their emotions and ensure their well-being.
A dog’s tail serves several important functions that contribute to their overall well-being and communication. It is not only an extension of their spine, but also a vital tool for expressing emotions, providing balance, and conveying valuable information to other dogs and humans.
Emotional Expression: A wagging tail is often associated with happiness and excitement, while a tucked tail is a sign of fear or submission. Dogs use their tails to communicate their emotions and intentions, allowing other dogs and humans to understand their state of mind.
Balancing Act: The tail acts as a counterbalance, helping dogs maintain stability and adjust their body position. It plays a crucial role in ensuring their coordination and agility, allowing them to navigate different terrains and perform various physical activities.
Communication Tool: Dogs use their tails to communicate with other dogs and humans, conveying important information about their intentions and mood. A high, stiff tail indicates confidence or aggression, while a low, relaxed tail suggests a friendly and approachable demeanor. Paying attention to a dog’s tail position can help us understand their social cues and avoid misunderstandings.
Warning Sign: A dog’s tail can also serve as a warning sign, indicating potential danger or discomfort. A tucked or stiffly held tail can be a signal that the dog is feeling anxious or threatened. Understanding these signals can prevent aggression or fearful reactions and promote a safe and harmonious interaction between dogs and humans.
Overall, a dog’s tail is a multifunctional appendage that plays a crucial role in their daily lives. It provides a means of expressing emotions, maintaining balance, communicating with others, and warning of potential danger. Recognizing and respecting the importance of a dog’s tail can enhance our understanding and connection with our canine companions, leading to a happier and more harmonious relationship.
A dog’s tail is a powerful and versatile communication tool that allows them to express a wide range of emotions and intentions. By observing the movements and positions of a dog’s tail, we can gain valuable insights into their current state of mind and overall demeanor.
One of the key ways a dog’s tail communicates is through wagging. While many people associate a wagging tail with happiness, it’s important to note that the meaning behind a wag can vary depending on the context. A relaxed and loose wag is typically a sign of a content and friendly dog, while a stiff and upright wag can indicate excitement or agitation.
The position of a dog’s tail also plays a significant role in their communication. A raised tail usually signifies confidence and a dominant posture, while a lowered or tucked tail suggests fear or submission. It’s essential to interpret a dog’s tail position in conjunction with their body language and other vocalizations to get a complete understanding of their message.
Furthermore, the speed and intensity of a tail wag can provide additional clues about a dog’s emotions. A slow and gentle wag may denote a calm and relaxed state, while a fast and vigorous wag can indicate high excitement or arousal. It’s crucial to approach and interact with a dog carefully, paying attention to these cues to ensure a positive and respectful interaction.
In addition to wagging, a dog’s tail can convey specific messages through different movements. For example, a slight twitch or wag that is predominantly to one side may express curiosity or interest in something. On the other hand, a rapid back-and-forth wag with the tail held high can indicate aggression or a potential threat.
Understanding how a dog’s tail communicates is vital for dog owners, trainers, and anyone who interacts with dogs regularly. By paying attention to their tail language and taking into account the overall context, we can better understand their needs and emotions and build stronger bonds with our canine companions.
Dogs have a highly sensitive tail that plays a crucial role in their communication and overall well-being. As a responsible dog owner, it is important to understand and address the specific needs and sensitivities associated with a dog’s tail.
Gentle Handling: When interacting with a dog, it is essential to handle their tail with care. Avoid pulling, twisting, or grabbing their tail, as this can cause discomfort or even injury. Instead, approach the tail gently, giving your dog a sense of security and trust.
Maintaining Good Hygiene: Regularly check your dog’s tail for any signs of injury, infection, or irritation. Keep the area clean and dry, paying attention to any discharge or foul odor. If you notice any redness, swelling, or persistent discomfort, consult with a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Preventing Tail Injuries: Dogs with sensitive tails can easily injure themselves in various situations. Pay attention to their surroundings, ensuring that there are no objects that can accidentally hit or trap their tail. Additionally, be cautious when closing doors or moving furniture, as their tail may get caught or squished.
Creating a Tail-Friendly Environment: Make sure your home environment is tail-friendly by removing any hazards that can cause injuries. Avoid sharp edges, low-hanging items, or cluttered spaces that can potentially harm your dog’s tail. Provide ample space for your dog to move around comfortably without the risk of knocking their tail against objects.
Utilizing Protective Measures: In situations where your dog’s tail is at risk, consider using protective measures, such as wrapping their tail with a soft bandage or covering. This can help prevent accidental injuries or further damage to their sensitive tail.
Regular Veterinary Care: Schedule regular check-ups with your veterinarian to ensure your dog’s tail health. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on your dog’s specific needs, addressing any concerns related to their tail sensitivity.
By following these guidelines, you can provide the necessary care and attention to your dog’s sensitive tail, ensuring their physical comfort, emotional well-being, and overall happiness.
A dog’s tail serves multiple purposes. It helps with balance and coordination while the dog is moving, acting as a counterweight. It also serves as a form of communication, conveying the dog’s emotions and intentions to other dogs and humans. Additionally, a dog’s tail can provide insight into its overall health and well-being.
A dog’s tail is sensitive because it contains numerous nerves and blood vessels. This sensitivity allows the dog to sense its surroundings and detect changes in the environment. It also enables the dog to use its tail for communication purposes, such as wagging it to express happiness or tucking it between its legs to indicate fear or submission.
Yes, tail sensitivity can vary among different dog breeds. Some breeds may have more sensitive tails, while others may have less sensitivity. This variation can be due to genetic factors and the overall anatomy of the tail. For example, dogs with long and thin tails may have more sensitive tails compared to dogs with short and stubby tails.
If your dog’s tail is injured or in pain, it is important to seek veterinary attention. Do not attempt to treat the tail yourself, as it could lead to further damage or discomfort for your dog. The veterinarian will be able to assess the extent of the injury and provide appropriate treatment, which may include pain medication, bandaging, or even surgery depending on the severity of the injury.
Why dogs lick your face? Dogs are known for their affectionate nature and one common way they show their love is by licking their owners’ faces. …
Read ArticleWhy dogs are more loyal than cats? Dogs have long been known as man’s best friend, and their loyalty is one of the key reasons for this title. …
Read ArticleWhy is my dog poop green and slimy? Seeing green and slimy poop in your dog’s stool can be alarming, but it is important to understand that …
Read ArticleWhy is the side of my dogs mouth swollen? Swelling on the side of a dog’s mouth can be a cause for concern for pet owners. There are several …
Read ArticleWhy is my dog panting when it isnt hot? Panting is a natural behavior for dogs, as it helps them regulate their body temperature. However, if your dog …
Read ArticleWhy is my senior dog barking all the time? As your dog ages, you may start to notice changes in their behavior, one of which may be excessive barking. …
Read Article